IMPORTANT MONTHLY UPDATES & ANNOUNCEMENTS
This month, we break down Duke Energy North Carolina’s rate overhaul, demonstrate how we handle the ACC export values for the California IOUs, highlight a new EUP feature to make calculating RTP values easier, and explain how to ensure that interval data usage matches the usage on bills.
Duke Energy – NC Rate Overhaul
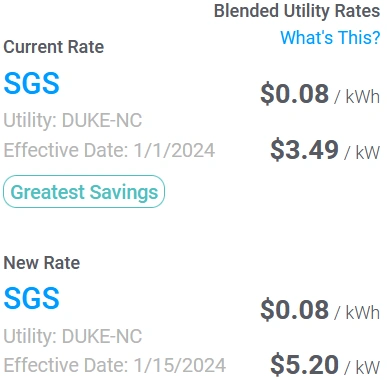
Duke Energy NC implemented two updates this month — one on January 1st and the other on the 15th. The first update included minor changes to a few riders, while the second update is part of a three-year rate increase that consists of an 8.3% increase this year, 3.3% in 2025, and 3% in 2026. Demand ratchets, TOU periods, and charge types are updated alongside the rate increase this month.
Base energy charges and demand charges increased for all rate schedules; however, the base energy charge increases were mainly offset by reductions to the Fuel Adjustment rider. For example, the blended demand rates for the popular Small General Service (SGS) rate schedule increased from $3.49/kW to $5.20/kW while the blended energy rates remained the same ($0.08/kWh) due to the offsets, which is evident in the following rate switch:
Before this update, Duke Energy utilized a 50% max demand ratchet for demand during the summer billing months. Now, most rate schedules use a 70% max annual demand ratchet and a 30kW fixed minimum ratchet. For more information regarding demand ratchets, please visitthis article from our ETB Help Center.
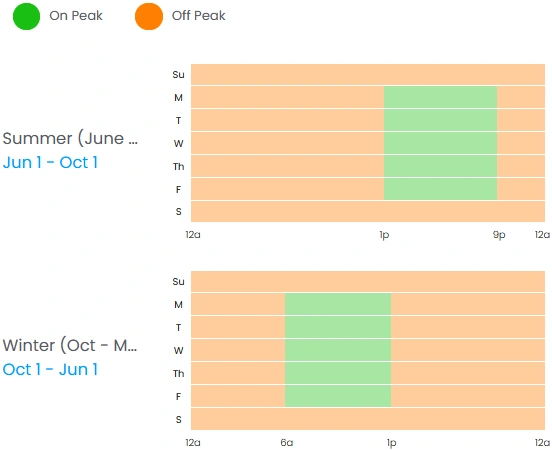
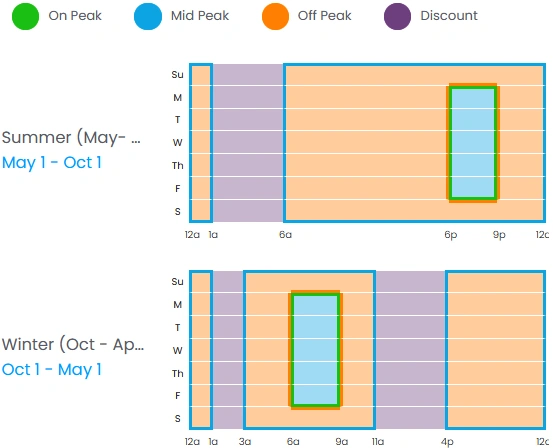
Another noticeable change is the update to TOU periods for rate schedule OPT-V. On-Peak hours used to be 1-9 p.m. for summer and 6 a.m.- 1 p.m. for winter, with all other hours considered Off-Peak. The new TOU periods include Mid-Peak hours with significantly higher demand charges and no base energy charges, and Discount hours with no demand charges and reduced base energy charges. The following images show the old TOU periods on the left compared to the new periods on the right:
ETB users working with rate OPT-V will want to input interval data rather than manually input bill usage so that ETB can distribute the correct kWh usage to the appropriate TOU period.
Lastly, this update changed the charge types for a few rate schedules. SGS now uses a Tiered charge type for energy instead of Tier Ceilings Vary with Demand, and rate schedule OPT-V now includes a TOU with Nested Tiers charge type with different tiered demand charges for the On-Peak and Mid-Peak periods, as can be seen below:
This update markedly changed the structure of these rate schedules and, depending on the type of customer, may have introduced new opportunities or challenges.
ACC Values for IOUs in 2024
The California IOUs recently released updated ACC values for generation and delivery exports. Our ETB rates utilize an entire year’s worth of ACC export values (Generation and Delivery) separated into two Real-Time Pricing (RTP) charge types.
For Direct Access customers on the Solar Billing Plan, we recommend that our users work within custom rate schedules rather than using the Retail Supply Function in the Energy Use Profile to account for their export values properly. These customers need to replace the generation-related ACC export values with their third-party supplier’s supply rate. To do this, follow the steps inthis video as we walk through this process.
FAQ: Why Doesn’t the Interval Data Usage Match the Bill Usage?
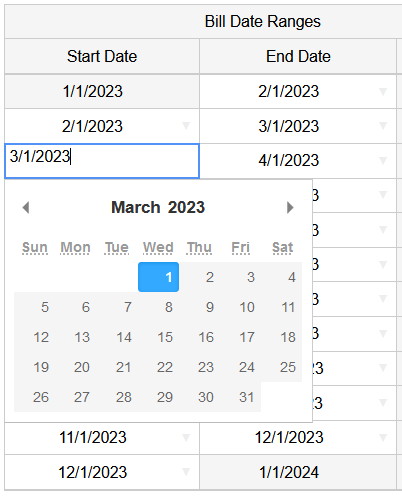
There are several reasons interval data consumption totals might appear to be calculated differently than bill totals when entered into the EUP. One reason is that the bill start and end dates don’t line up. Billing periods can vary depending on the meter read cycle a customer is placed on, and it’s essential to specify the exact start and end dates in the Energy Use Profile. The “Bill Date Ranges” columns have dropdown arrows on the right of the cell that you can select to pick the exact dates. Matching these dates to your bills is one likely solution to getting the consumption totals from your interval data to line up with the bills.
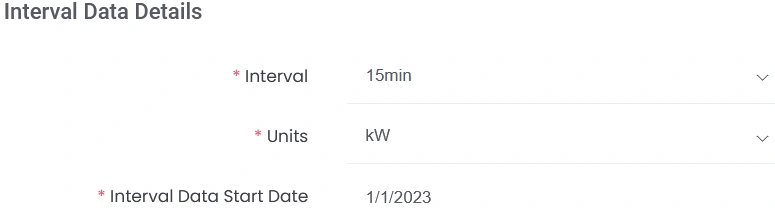
Another possible solution is to double-check the format of the interval data because sometimes the interval data is formatted in kW units instead of kWh, which is the default unit selection when uploading interval data in ETB:
Ensuring that the unit selection matches the data format when uploading interval data is critical. It is also important to follow the instructions when uploading the interval data to ensure that daylight savings time is accounted for in the data.
Following these steps can potentially reduce any discrepancies in energy consumption when comparing interval data to bill usage.
Did You Know? – You Can Now Refresh RTP Energy Charges in the EUP
We recently added a new feature that allows users to refresh energy charges in the Energy Use Profile for rates with RTP charges where bill usage is manually entered. Previously, users needed to save the Energy Use Profile before the energy charges were updated, as it caused ETB to take an extra step to take flat energy consumption entered from bills and calculate it with hourly interval periods from the load profile. Clicking the new “Refresh Energy Charges” button allows you to input bill usage and have ETB run the detailed load profile calculations without the need to close and reopen the EUP: