Massachusetts consistently ranks as one of the best states in the country for going solar. According to Greentech Media’s 2019 Research Solar Market Insight Report, the Bay State ranks as a top 10 state for installed solar capacity nationwide. At the end of 2019, the Commonwealth had almost 3 gigawatts (GW) of capacity installed, spread across nearly half a million installations. Additionally, Massachusetts has already begun to emerge as a leading state for energy storage system deployments. The most recent U.S. Energy Storage Monitor Report projects the commonwealth to be a top 10 state for storage deployments over the next 5 years in both the Front-of-the-meter and Commercial & Industrial (C&I) segment. The strong economic value proposition for solar and storage in Massachusetts has been driven by favorable state-level incentive programs, relatively high retail electricity rates, and a supportive state legislature. The image below, from ISO New England, shows a statewide heat map of installed solar capacity by municipality.
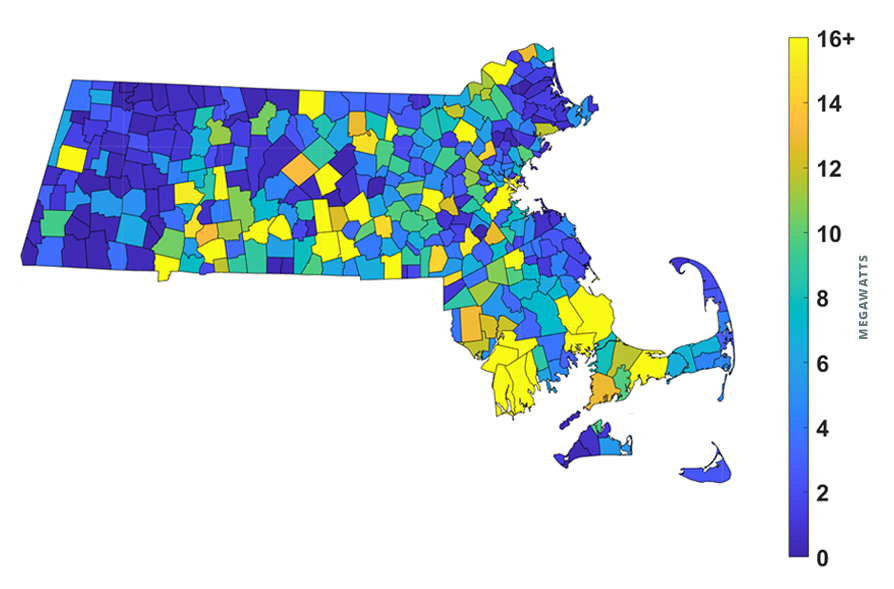
Source: ISO New England
The Massachusetts market has evolved significantly over the last decade. It’s been a unique state market in that it has successfully launched and cycled through a number of different incentive programs from SREC I and II, to a phased sunsetting of their Net Metering (NEM) program, to the SMART program, which is currently undergoing a redesign, and most recently the pending launch of the innovative new Clean Peak Standard program. All of the legacy incentive programs in Massachusetts to date have had widespread customer uptake and adoption. What got the market to where it is today is ending, and in many ways, a new era of solar + storage in the Commonwealth is now beginning. We will unpack the new Massachusetts incentive programs in future blogs. In this article, we summarize important industry acronyms, entities, and programs and provide weblinks to the best online resources.
Key Acronyms
ACP (Alternative Compliance Payment): Within the new Clean Peak Standard incentive program, to keep ratepayer costs under $0.005/kWh, the DOER proposed an Alternative Compliance Payment rate of $45 per MWh which acts as a ceiling. This rate will remain constant until 2024, declining by $1.54 per MWh thereafter through 2050.
AOBC (Alternative On-Bill Credit): With the state having effectively phased out net metering for new large solar projects, a new mechanism under the Massachusetts SMART Solar Program will allow solar projects to virtually send the monetary value of excess production to other electric accounts. This value is called an Alternative On-Bill Credit, or AOBC.
BTM (Behind-the-Meter): Systems connected behind a customer billing meter. A Generation Unit that serves On-site Load other than parasitic or station load utilized to operate the Generation Unit.
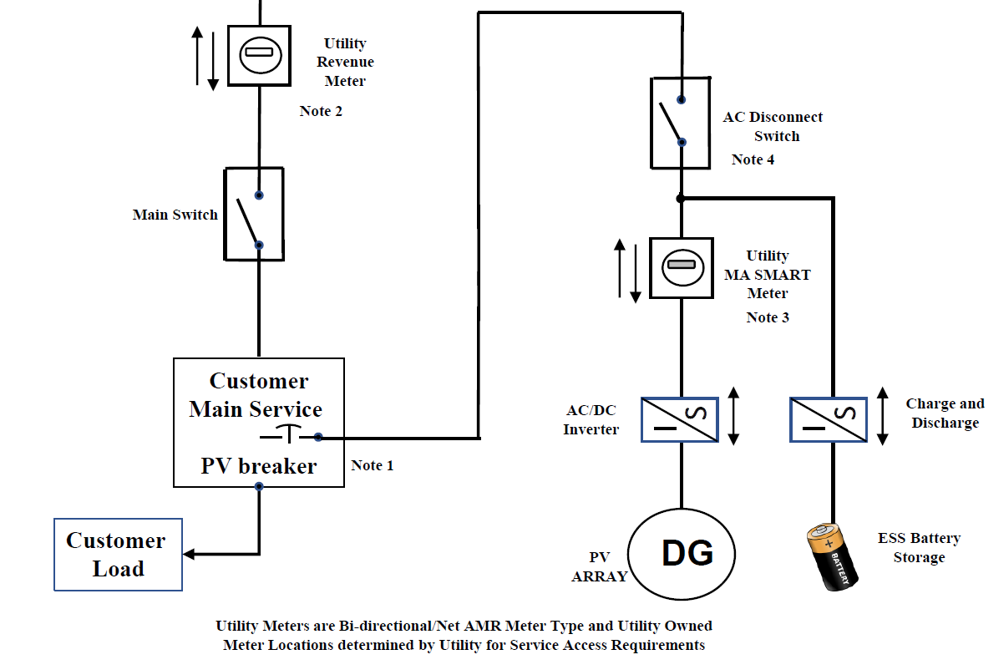
CPEC (Clean Peak Energy Certificates): Within the new Clean Peak Standard incentive program, an eligible, qualified resource will generate Clean Peak Energy Certificates (CPECs) according to its performance over the duration of the four-hour peak period of a particular day. Multipliers will be applied based on season and daily time window.
CPS (Clean Peak Standard) or CPES (Clean Peak Energy Standard): Incentive program under development which was passed in legislation in 2018. It was designed to provide incentives to clean energy that creates credits for clean energy delivered during pre-specified time windows identified as peak hours for a given season. Utilities in the state must obtain clean peak credits equal to a percentage of total electricity delivered in the year, starting at 1.5 percent in 2020 and growing annually by 1.5 percent.
DR (Demand Response): Demand Response is a program through which customers reduce their electricity consumption in response to either high wholesale prices or system reliability risks. Demand Response customers are paid for performance based on wholesale market prices. The ISO New England regional grid operator administers this program.
EDC (Electric Distribution Company): The company that owns the power lines and equipment necessary to deliver purchased electricity to the customer.
FTM (Front-of-the-Meter): Systems connected in front of a customer’s billing meter, often referred to as a Standalone Solar Generation Unit. A Solar Generation Unit that serves no associated On-site Load other than parasitic or station load utilized to operate the Generation Unit or coupled Energy Storage System.
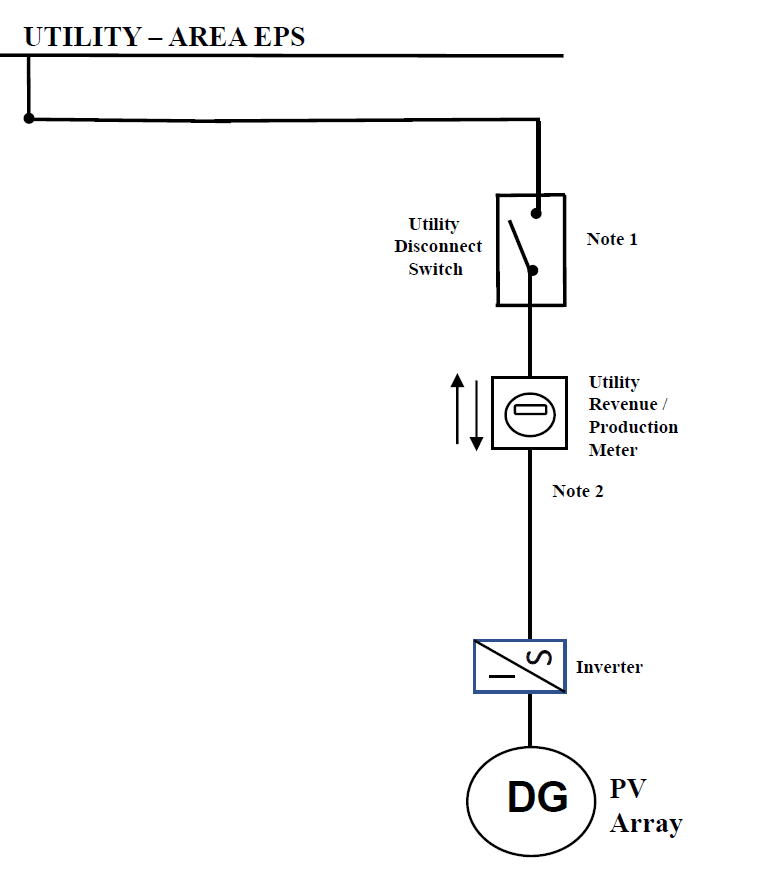
Image: Front-of-the-meter diagram | Source: Eversource
RGGI (Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative): A program in which Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic states cooperate to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. In Jan. 2007, Massachusetts joined RGGI, a cooperative effort by Northeast and Mid-Atlantic States to reduce CO2 emissions from large fossil-fueled power plants. RGGI is a regulatory program that uses market incentives instead of top-down legislation to combat climate change.
SMART (Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target Program): A long-term, sustainable solar + storage incentive program designed to promote cost-effective solar development in the Commonwealth. The successor to the SCREC II program and current state-managed solar incentive program.
SREC Solar Carve-Out Renewable Energy Certificate): The SREC I and SREC II programs were born out of SB2768, known as the Green Communities Act of 2008. These programs successfully carried Massachusetts to its goal of installing 1,600MW of solar by 2020 and were closed upon reaching their goal in November 2018.
Key Entities
DOER (Massachusetts Department of Energy Resources): A state agency that develops and implements policies and programs aimed at securing the adequacy, security, diversity, and cost-effectiveness of the Commonwealth’s energy supply to create a clean, affordable, and resilient energy future. The DOER strives to maximize the development of clean energy resources and support Massachusetts’ clean energy companies and spur clean energy employment.
DPU (Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities): An agency that oversees investor-owned electric, natural gas, and water companies in Massachusetts. The DPU is responsible for monitoring service quality, regulating safety in the transportation and gas pipeline areas, and for the siting of energy facilities.
ISO-NE (Independent Systems Operator New England): The regional transmission organization for most of New England, which is authorized by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission to exercise for the New England Control Area and maintain the functions required for keeping electricity flowing and to ensure that the region has reliable, competitively priced wholesale electricity.
(MassACA) Massachusetts System of Assurance of Net Metering Eligibility: The entity required by the Massachusetts DOER: (1) to track the aggregate capacity of net metering facilities; and (2) to provide host customers and other stakeholders with an assurance, before beginning construction, that their facility may participate in the net metering program. The Cadmus Group currently serves as the third-party administrator of MassACA.
NEPOOL GIS (The New England Power Pool Generation Information System): Issues and tracks certificates for all MWh, including CPECs, of generation and load produced in the ISO New England control area to enable REC transactions. NEPOOL GIS is operated by the New England Power Pool and is administered by APX.
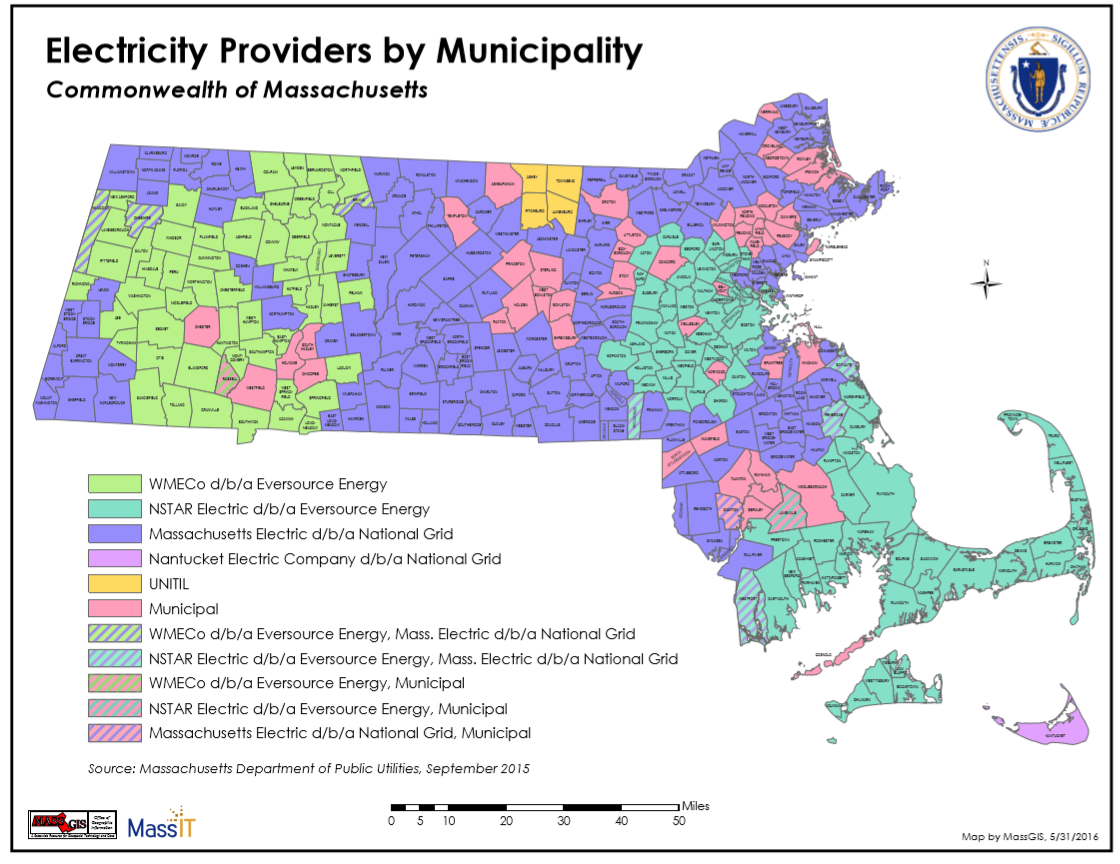
EDC Service Areas
Fitchburg Gas and Electric Light Company, aka Unitil
NSTAR Electric & Western Massachusetts Electric Company, aka Eversource Energy
Key References & Weblinks
MA Net Metering:
SMART:
- SMART
- SMART Emergency Rulemaking
- BTM Value of Energy (Excel workbook)
- Energy Storage Calculator (Excel workbook)
Clean Peak Standard:
Demand Response:
Miscellaneous:
Quinn Laudenslager is a senior manager on our Technology and Product Operations Team. He is based in Tennessee.



