Effective solar analysis tools are essential for providing insights into the cost and performance of potential solar and storage projects, but how reliable is their data and how accurate are these tools? Tools like ETB Developer employ sophisticated algorithms and utilize a wide range of data to simulate solar energy production and system performance. Most tools utilize data that includes energy consumption patterns, solar generation data, and system design. In this blog, we’ll go step-by-step through a solar analysis, consider the type of data used, and determine how accurate these tools can be.
Energy Usage Profile
The first step of a solar analysis often involves an Energy Usage Profile (EUP), which is a detailed representation of how energy is consumed at a site or by a system over time. ETB Developer will use the EUP to help understand patterns of energy consumption, identify peak usage periods, and potentially optimize energy efficiency. Some solar analysis tools will request energy consumption data from customer bills to create an EUP; however, interval data collected from a smart meter is much more granular and provides greater detail in identifying the exact peak times. This difference in energy consumption inputs could result in slightly skewed projections and estimated savings.
Another important, yet often overlooked component, of an EUP is the rate tariff. Every electric utility customer pays customer, energy, and demand charges in some shape or form. The most accurate tools will consider the exact rate schedule a customer is on and build the analysis from that. A customer’s rate schedule determines not only what they are billed for energy consumption but also how they are billed. Some rate schedules have time-of-use periods with different energy prices for energy consumed at certain hours of the day; other schedules may have tiered energy prices based on the consumer’s monthly, seasonal, or annual demand. However, many solar analysis tools don’t even consider specific rate schedule data; instead, many choose to utilize generalized regional electricity data that lacks specificity and results in less-than-accurate projections and estimates. ETB Developer is the only solar analysis software that has an in-house utility rates team that updates and analyzes rate tariffs across the country each month to ensure the utmost accuracy. A tool that considers the exact rate schedule a customer is on will be far more accurate at estimating savings.
Lastly, another factor to consider is the utility’s net metering tariff. Some utilities offer net metering with exports valued at the retail rate, while other utilities value exports at a wholesale rate that is less than the retail rate. Whatever the case, including the net metering tariff into the analysis is crucial to determine how much value a client can get out of a proposed system. The rate tariff information, including the structure and prices, as well as the utilities net metering tariff are important factors to consider in any EUP as all these pieces of data can greatly influence payback periods or even determine whether a project is worthwhile.
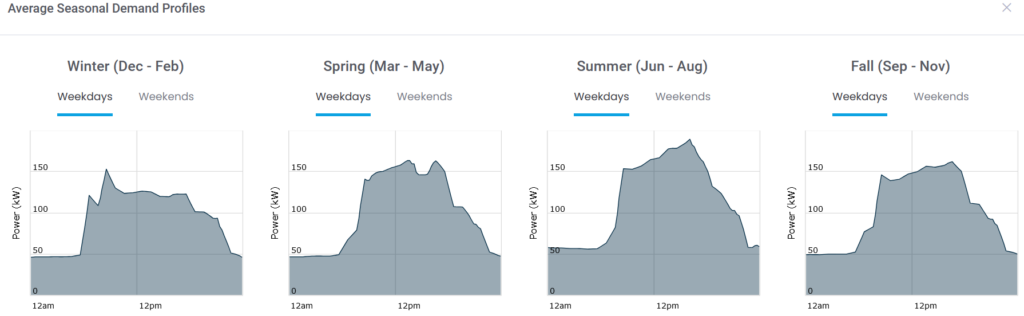
Figure 1: A Mapping of Seasonal Loads for an EUP in ETB Developer
Solar Generation Data and System Design
Once the EUP is set up, the next considerations are the solar generation data and system design. Solar generation data includes factors like solar irradiance, temperature, weather conditions, and much more and is used by a solar analysis tool to simulate how much solar energy a proposed system will produce and estimate what kind of savings can be expected. Of course, the simulations these tools run are only as accurate as the data they use, so quality tools utilize high-resolution, up-to-date solar irradiance and weather data from reliable sources like weather stations and satellites. Some tools that prioritize quick estimates draw on generalized global data, but this data lacks the specificity of regional or local sources, resulting in less accuracy.
Next is the design of the system. The design includes data points like roof measurements, desired offset, shading analysis, system losses, and more. The design is where the most user input lies and so is inherently prone to inaccuracies, especially if measurements of the site are done by hand. For this reason, a good solar analysis tool will include satellite imaging or even drone technology to generate 3D models of the site that can account for nearly every factor that influences a system’s performance.
The EUP, solar generation data, and system design are all integral components of any solar analysis, and the data we covered here is just the tip of the iceberg. Other things to consider are financial incentives, energy credits, the possibility of rate switches, and more. Ultimately, the more data points that a solar analysis tool considers, and the greater the reliability of the data, the more accurate and comprehensive its results will be. That is why we are proud to offer ETB Developer as an accurate and reliable tool to aid users in creating a successful solar and financial analysis.
What Sets ETB Developer Apart from the Rest?
We’re obsessed with accuracy at Energy Toolbase; that’s why we work with the highest quality data, have integrations with top-of-the-line products, and have an in-house utility rate team that guarantees the most accurate rate data possible.
There are several options available to our ETB Developer users for uploading or importing high-quality energy consumption data into an EUP. Users can input bill data, upload interval data, or utilize the Green Button Data feature to easily and securely fetch a client’s annual energy consumption data. We also have UtilityAPI integration that makes the process of collecting consumption data even easier and quicker, ensuring little downtime when working on projects. All these options are available to users to guarantee the most accurate results possible when analyzing a project.
Figure 2: Options for Uploading Energy Consumption Data into an EUP
For solar generation data, users can upload their own solar production data or utilize PVWatts, one of the most trusted sources for solar production data backed by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory. PVWatts provides energy generation estimates for energy systems throughout the world by incorporating potential energy production, local weather data, and performance metrics based on site-specific data into its simulations.

Figure 3: Solar Generation and Design Options for ETB Developer
We also offer our users integrations with respected and innovative solar design tools like Helioscope and Scanifly. Helioscope offers advanced system design tools to users and Scanifly uses drone technology to generate 3D models with higher resolution than typical satellite imaging. These integrations enable ETB Developer users to seamlessly import detailed solar designs directly into their ETB Developer analysis.
Our commitment to accuracy is also why we have a dedicated in-house utility rates team that manages our vast database of rate schedules. While many other solar analysis tools utilize regional electricity rates for their calculations, our in-house rates team creates up-to-date utility-specific rate schedules that ETB Developer uses to calculate demand charges, account for time-of-use periods, and predict precise energy production and consumption. ETB Developer’s detailed rate data and avoided cost analysis combined with high-quality PV generation data and design tools give unparalleled depth and accuracy to solar proposals.
As a solar and financial analysis tool, ETB Developer blends advanced algorithms, high-quality data, and robust financial modeling, making it an invaluable tool for anyone looking to invest in solar and storage technologies. Sign up for a 14-Day Free Trial and see how ETB Developer’s powerful features can enhance your solar and energy storage projects today!



