IMPORTANT MONTHLY UPDATES & ANNOUNCEMENTS
This month we cover rate cases for Idaho Power, Public Service Company of New Mexico, and Con Edison, highlight the addition of Hawaiian Electric’s Shift & Save rates to our database, and explain the difference between PG&E’s B-1 and B-6 rate schedules.
Idaho Power’s First General Rate Case in 13 Years
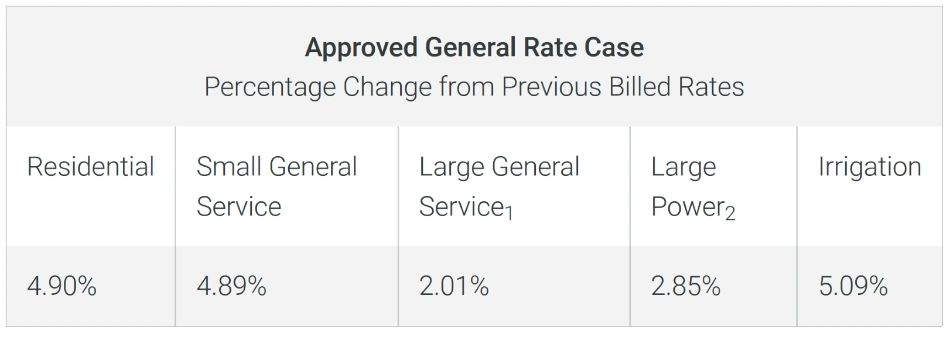
Idaho Power’s first general rate case since 2011 was recently approved and implemented. The rate case calls for an overall rate revenue increase of $54.7 million with specific percentage changes that vary for different customer classifications:
Along with these rate increases, Idaho Power made changes to its on-site generation compensation structure from full retail net metering to a real-time net billing plan that bills customers for all imported kWh consumed and credits them for all kWh exported. Exported energy is now compensated at a time-differentiated export credit rate (ECR) with netting that occurs after all imports and exports are given a monetary value. We added new TOU periods to all rate schedules to account for the ECRs. These TOU periods include On-Peak hours from 3 p.m.-11 p.m. Monday through Saturday during the summer season with all other hours deemed Off-Peak. The ECRs range in value from $0.04/kWh to $0.17/kWh depending on the hours of the day.
Public Service of New Mexico’s New Rate Case
PSNM’s rate case went into effect this month with several changes driven by PSNM’s carbon-free initiatives, the closure of the San Juan coal plant and expiration of leased energy from the Palo Verde nuclear plant, and adjustments for inflation. The overall system average rate increase is 8.77%. Energy rates for most rate schedules decreased, and in some cases they decreased drastically. For example, rate 3C’s base energy charge reduced by 34%; however, the demand charge increased by almost 100%. The summer demand charge for rate 3C went from $8.1/kW to $16.18/kW and the winter demand increased from $6.05/kW to $12.09/kW. Other commercial and industrial rate schedules show similar changes — lower energy charges but higher demand charges.
Con Edison Base Rate Update
Con Edison recently implemented several rate updates and changes to rate structures. For example, the popular EL 9 rate schedule has a new $66 customer charge and a flat rate demand charge type instead of the previous tiered structure. We performed a rate switch from an EL 9 rate with a 12/1/2023 effective date to a 2/1/2024 effective date using a Large Office load profile and found that winter bill totals were 17% lower, summer bill totals were 2% lower, and the overall annual bill total was 12% lower. The customer paid slightly more for demand charges in the summer season, but these additional costs were more than offset by a significant reduction in energy charges. The total kWh charge (excluding hourly pricing) for the current winter season decreased from $0.029644/kWh to $0.00412/kWh.
FAQ: What is the Difference Between PG&E’s B-1 and B-6 Rates?
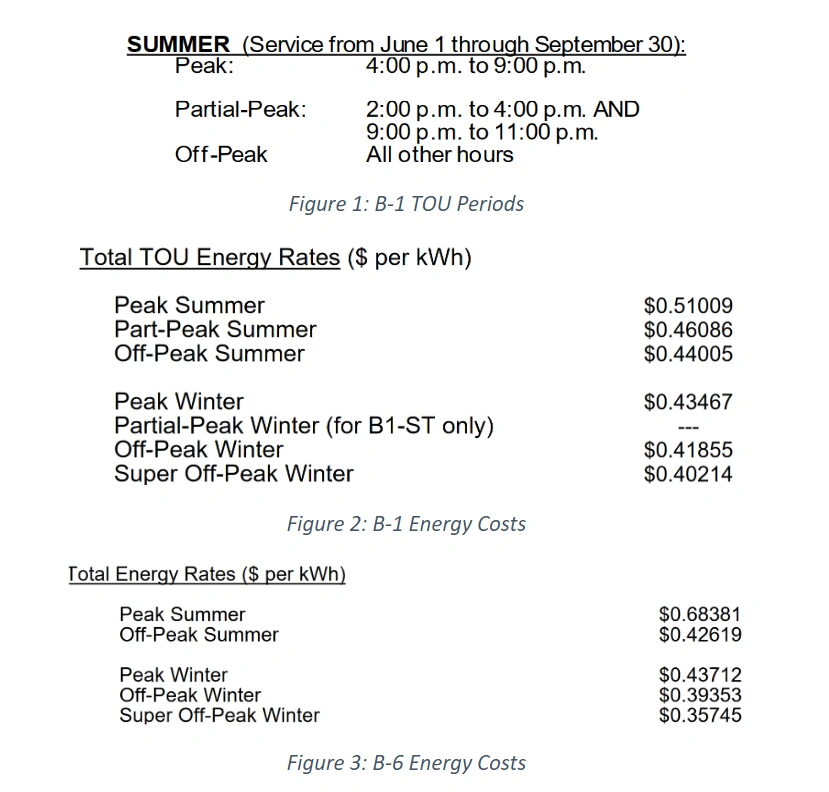
PG&E’s B-1 and B-6 rate schedules are very similar: They are both for small business customers with demands less than 75kW; however, there are a few minor differences between the two that could result in savings depending on a customer’s consumption patterns. These two rate schedules have slightly different TOU periods and costs for energy. Both rate schedules have the same Peak and Off-Peak hours, but B-1 has Partial-Peak TOU hours for the summer season. B-6 also has lower costs for Off-Peak and Super Off-Peak energy consumption but significantly higher costs for On-Peak usage:
Comparing the annual bill totals for two hypothetical customers (B-1 and B-6) with a Small Office load profile, we found that customers on B-6 can save 4-6% in the winter months because of the reduced Off-Peak and Super Off-Peak costs, but that they can spend 5-6% more in the summer months because of the significantly higher On-Peak costs. B-6 favors customers with high consumption during the Off-Peak and Super Off-Peak hours with low consumption during the On-Peak hours. If a customer cannot shift their summer usage from the 4 p.m.-9 p.m. On-Peak hours to the Off-Peak hours, then schedule B-1 may result in more savings due to the On-Peak charges being $0.17/kWh lower.
Ultimately, the question of which rate schedule provides more savings comes down to consumption habits. We recommend our ETB users perform a rate switch in a Proposal to see which rate schedule is more advantageous for their customer based on their consumption.
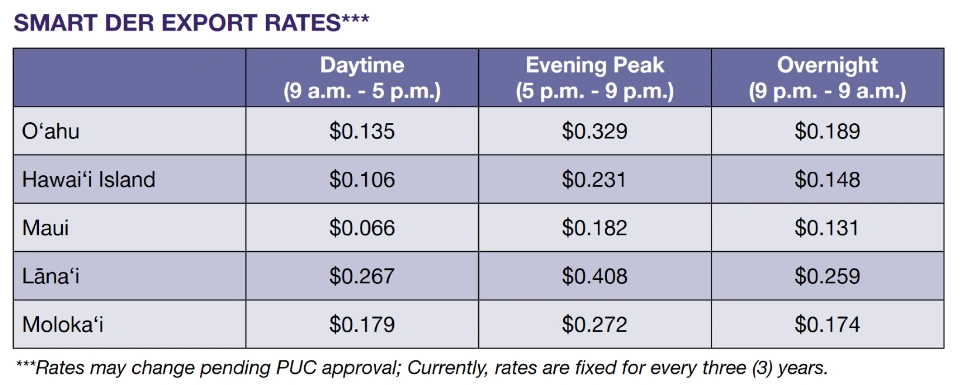
Did You Know? – Shift & Save Rates for Hawaiian Electric Now Available
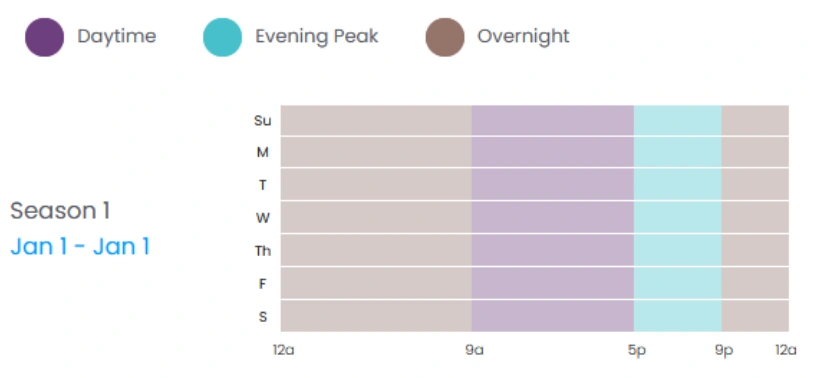
In ourDecember 2023 newsletter, we mentioned that Hawaii electric utilities were introducing new Shift & Save pilot rates with new TOU periods in February 2024. Many of our ETB users have expressed interest in modeling these new rates, so our Utility Rates Team has added the following Shift & Save pilot rates: ARD TOU R, ARD TOU G, and ARD TOU J. The naming convention for these rates comes from the tariff sheets that call these, “Advanced Rate Design” rate schedules. These rates have TOU periods labeled Daytime (9 a.m.-5 p.m.), Evening Peak (5 p.m.-9 p.m.), and Overnight (9 p.m.-9 a.m.):
These rates also featureSmart DER Export rates and allow customers to receive time-varying compensation for exported energy. This new export program is available for both residential and commercial customers, features no specific project size limits, and allows new customers the chance to lock in the following export rates for seven years:
Customers must switch to the new Shift & Save rate schedules to participate in the Smart DER program.